The Deutsche Bank study does not seem to be available for free, it has been quoted on news only. So, the assumptions are not clear.
Assuming Trump’s universal, 10% baseline tariff represents a “top up” of existing rates for those imports currently below that level, the bank’s economists expect a 120 basis point increase in headline personal consumption expenditure, or PCE, and a 140 basis point uptick in core PCE prices, they wrote. If the average tariff rate on Chinese imports were to jump from 12% to 50%, they added, that would raise headline and core PCE prices by some 20 to 30 basis points.
I saw some days ago a presentation by Goldman Sachs, and they estimated a similar price level increase increased of ~1.1%.
These are their assumptions:
- US imposes a 10% tariff on all imports, and other countries retaliate by raising tariffs by 10% too.
- Additional tariff revenue is recycled into tax cuts, so is fiscally neutral.
- Trade policy uncertainty rises to the levels seen at the peak in the 2018-2019 trade war.
A 1%-2% increase in the price level seems manageable under normal circumstances, but in the current environment, even a slight rise in inflation could be viewed negatively. This could potentially put pressure on the Federal Reserve to take action.
We also do not know the potential indirect effects as you mentioned in the labor market.
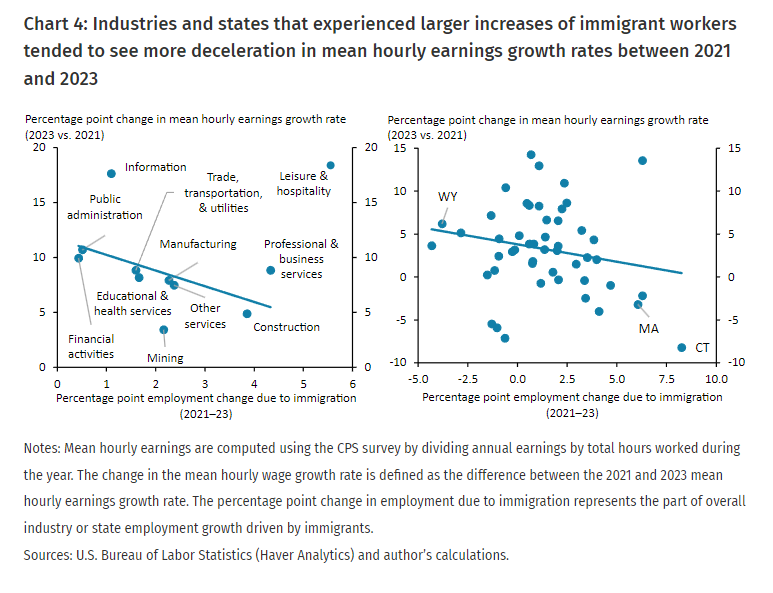
At the same time, I think immigration policies could have a more significant impact than tariffs. Although I haven’t found studies estimating this impact.
Employment has expanded largely due to foreign workers rather than nationals. Any disruptions to labor supply could lead to wage increases in sectors more dependent on immigration, eventually causing inflation.
- According to the Kansas Fed, wage growth slowed by roughly 0.7 percentage points for every 1.0 percentage point increase in an industry’s immigrant employment growth.
In the end, its the combined impact of these three policies, and not isolated. They have the potential to increase output and labor demand while simultaneously disrupting its supply. Changes in labor market dynamics could be the most significant factor imo.