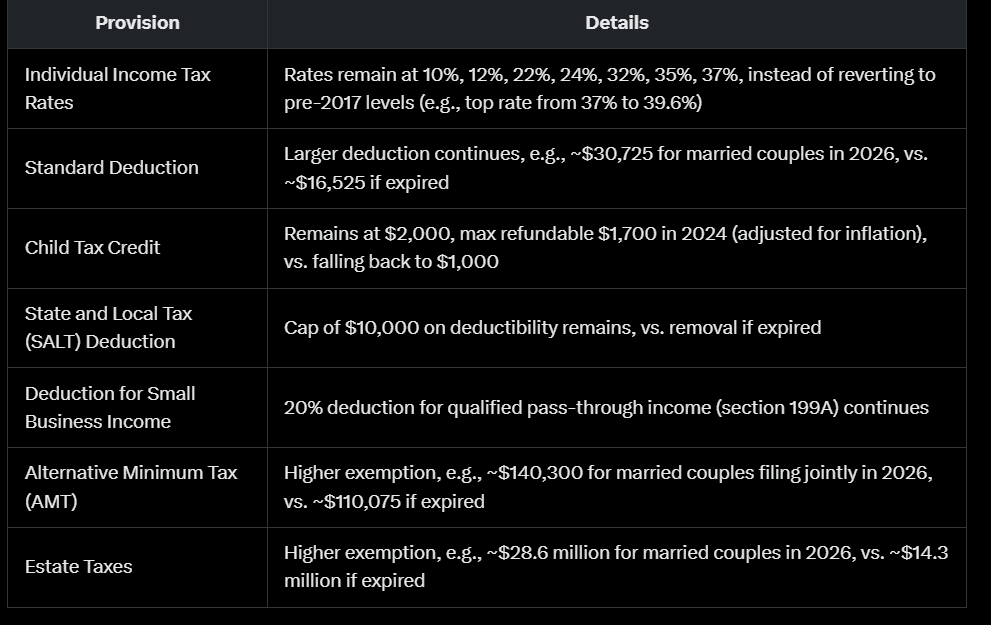
The tax cuts for 2025 are primarily focused on extending the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017, which is set to expire at the end of the year
New tax exemptions, such as no taxes on tips, overtime pay, and Social Security benefits for retirees and a lower tax rate for domestic manufacturers (15%), may also be part of the package, reflecting President Trump’s campaign proposals.
-
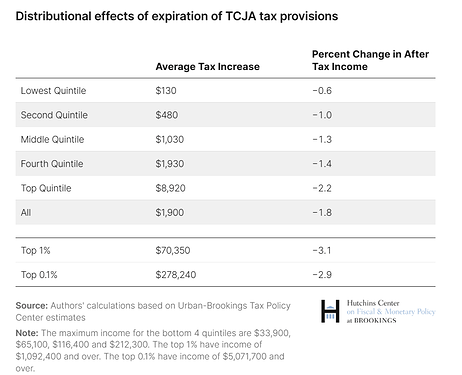
If Congress allows the TCJA to expire as scheduled would result in more than 62 percent of tax filers experiencing tax increases in 2026.
-
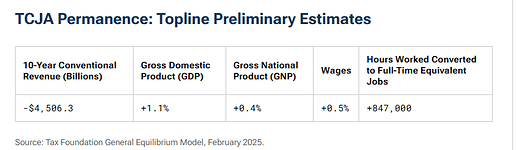
Extending the expiring 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) would reduce federal tax revenue by $4.5 trillion from 2025 to 2034. The Tax Foundation estimates:
- Long-run GDP would rise 1.1%, offsetting $710 billion (16%) of revenue loss.
- Long-run GNP would rise just 0.4%, as more interest payments go to foreign holders of U.S. debt.
- Average after-tax incomes would increase by 2.9% (3.4% dynamically) in 2026.
On February 25, 2025, the House passed a budget resolution allowing up to $4.5 trillion in tax cuts if paired with $1.7 trillion in spending cuts—adjusting the cap up or down based on actual cuts. The Senate’s resolution, passed February 21, allows no tax cuts at all.
@Aron Please note this is mostly extending already-in-place tax rates, it isn’t necessarily an additional tailwind to account on models, as most companies would not see any change. In reality, if the tax cuts are not extended, it could be a headwind as tax rates and benefits will return to 2017 levels, and lower income and earnings. (See image below)