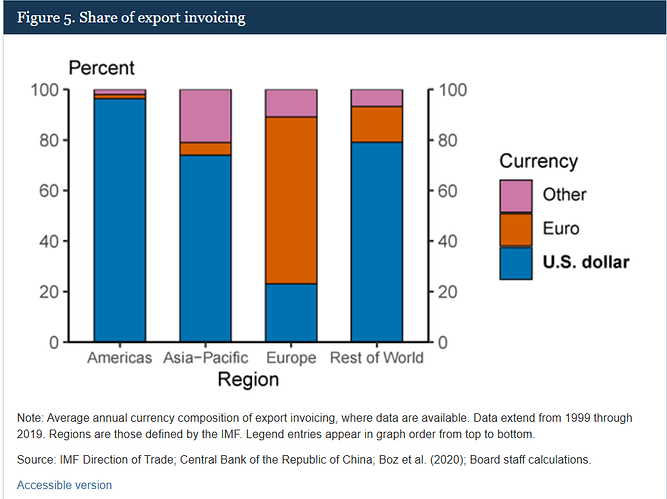
Currency invoicing refers to the choice of currency used to denominate and settle international trade transactions. When two countries engage in trade—say, exports and imports of goods or services—they must agree on a currency in which the invoice (i.e., the bill) will be issued. This currency is also typically used for payment settlement.
There are generally three types of invoicing practices:
- Producer Currency Pricing (PCP): Exports are invoiced in the currency of the exporting country.
- Local Currency Pricing (LCP): Imports are invoiced in the currency of the importing country.
- Dominant Currency Pricing (DCP): A third, globally dominant currency (most often the US dollar, sometimes the euro) is used regardless of the countries involved.