Topic to discuss developments in the global economy, and also make comparison in different metrics between different countries or regions
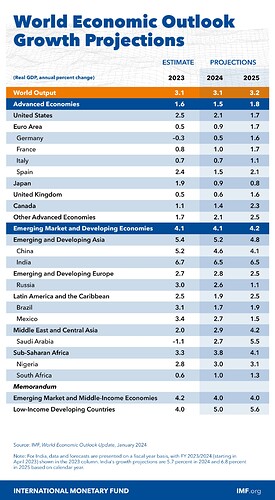
There are IMF projections for 2024.
These usually have revisions throughout the year, is not to be taken as 100% accurate
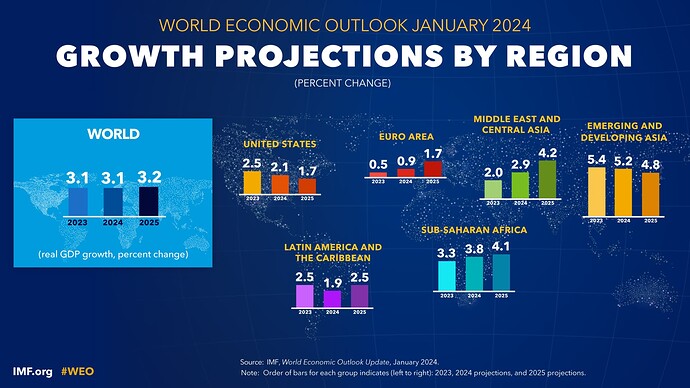
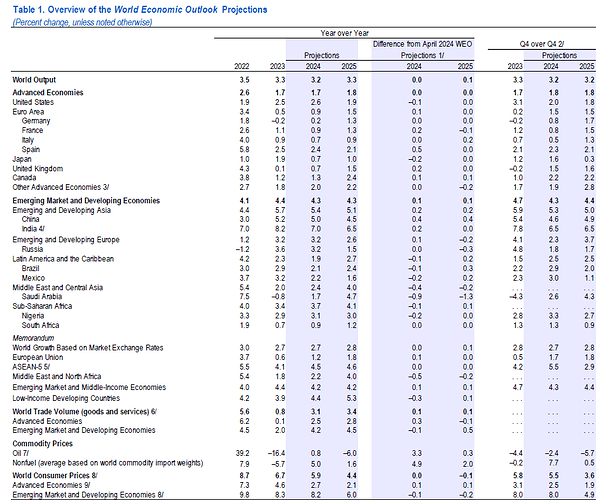
Global growth is projected at 3.1 percent in 2024 and 3.2 percent in 2025, with the 2024 forecast 0.2 percentage point higher than that in the October 2023 on account of greater-than-expected resilience in the United States and several large emerging market and developing economies, as well as fiscal support in China.
Upside risks
- Faster disinflation
- Slower-than-assumed withdrawal of fiscal support
- Faster economic recovery in China
- Artificial intelligence and supply-side reform
Downside risks
- Commodity price spikes amid geopolitical and weather shocks
- Persistence of core inflation, requiring a tighter monetary policy stance
- Faltering of growth in China
- Disruptive turn to fiscal consolidation
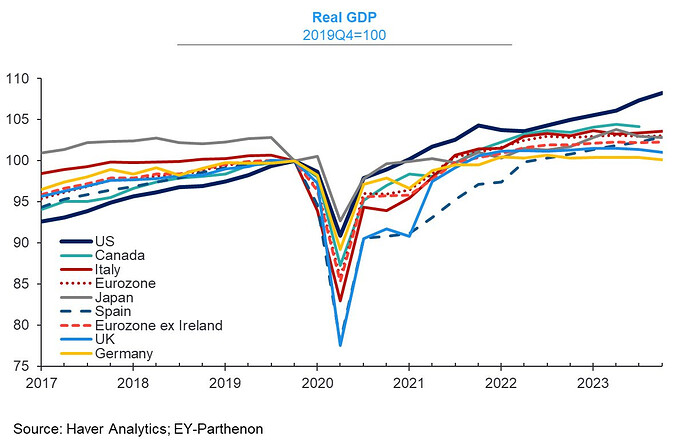
The US was the one with the lowest growth before the pandemic, and now is the one outperforming.
https://twitter.com/GregDaco/status/1759558953581891760/photo/1
Q2 Global Growth Update
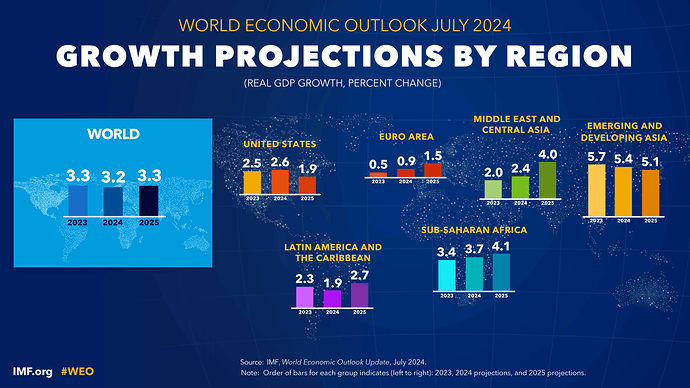
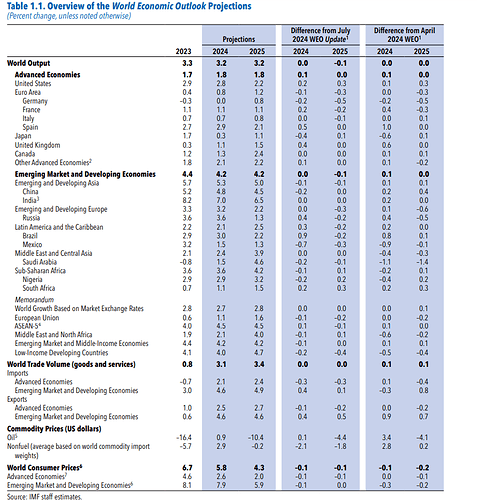
- The global economy is projected to grow by 3.2% in 2024 and 3.3% in 2025, aligned with April 2024 forecasts.
- World trade growth is expected to align with global GDP growth, recovering to about 3.25% annually in 2024-25.
- In advanced economies, the revised forecast is for the pace of disinflation to slow in 2024 and 2025. That is because inflation in prices for services is now expected to be more persistent and commodity prices higher
Risks:
- Upside risks to inflation persist due to services price inflation and potential geopolitical tensions.
- The prospect of higher-for-longer interest rates raises external, fiscal, and financial risks, particularly for emerging markets.
- A carefully sequenced policy mix is crucial to manage inflation, rebuild economic buffers, and ensure fiscal consolidation.
- Need to manage currency and capital flow volatility, utilize reserves prudently, and implement macroprudential policies to mitigate vulnerabilities.
Q3 2024 IMF Update: Global growth is expected to remain stable yet underwhelming. At 3.2% in 2024 and 2025.
Upgrades to the forecast for the United States offsetting downgrades to those for other advanced economies, in particular, the largest European countries.
Persistent structural headwinds, such as population aging and weak productivity, are holding back potential growth in many economies.
Although investment is expected to pick up and productivity growth is also expected to see some normalization, the continued demographic drag is likely to produce an offsetting effect.
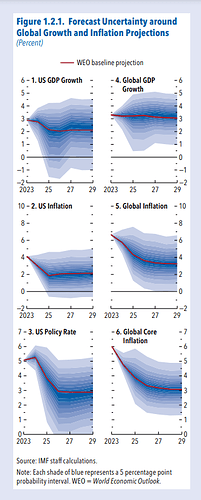
- For many advanced and emerging market economies, the five-year-ahead forecast is weaker than the one-year-ahead forecast
- The five-year-ahead forecast for global growth stands at 3.1 percent, indicating continued mediocre medium-term prospects relative to prepandemic forecasts.
Risks to the Outlook are currently Tilted to the Downside
The risk of global growth falling below 2 percent—an outcome that has occurred only five times since 1970—in 2025 is now assessed at 17 percent, compared with 12 percent in April, in part because the risk of a recession in the United States has increased moderately. Risks for global inflation are considered broadly balanced.
- The probability of US growth falling below 0.8 percent in 2025, corresponding to a short-lived US recession starting in the fourth quarter of 2024 is about 25 percent. That is a modest increase from the risk of recession in the April 2024 17%
- The risk of average US headline inflation falling below 1.5 percent in 2025 is assessed at about 40 percent; the risk of the federal funds rate falling below 3 percent for 2025 is about 28 percent.
Downside Risks:
- Recent rate hikes could slow growth and increase unemployment faster if their impact on the economy strengthens unexpectedly.
- Persistent inflation may push consumers to adjust expectations, leading to tighter financial conditions, lower confidence, and slower recovery.
- Some emerging markets and developing countries are still vulnerable to a repricing of risk high in their sovereign debt, with limited fiscal flexibility, risking economic downturn if forced to consolidate budgets.
- China’s property sector could experience deeper contractions, with falling prices, sales, and investments. This could cause domestic demand to falter, with negative spillovers to both advanced and emerging market economies given China’s rising footprint in global trade
- Commodity prices may spike again due to climate events, regional conflicts, or geopolitical tensions.
- Protectionist policies could harm global trade, disrupt supply chains, and slow growth by limiting innovation spillovers.
- Rising inflation, taxes, and inequality may drive social unrest, weakening growth, especially in countries with limited policy buffers.
Upside Risks:
- Advanced economies might accelerate public investment for green transitions, infrastructure, and tech, potentially boosting private investment, demand, and trade recovery.
- Speedier structural reforms to boost labor participation, reduce market inefficiencies, and spur business innovation could drive stronger medium-term growth.
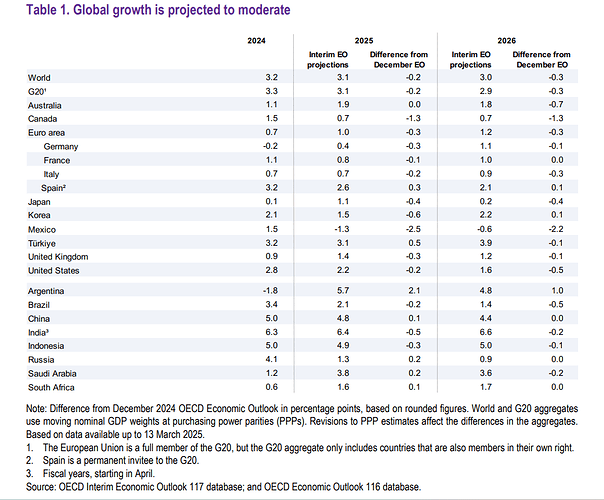
The OECD lowered its global economic growth forecast due to escalating U.S. trade tensions, expecting global GDP to slow from 3.2% in 2024 to 3.1% in 2025 and 3.0% in 2026
-
North America expected to be hit hardest:
- U.S. growth forecast cut to 2.2% in 2025 and 1.6% in 2026, cutting its forecasts from 2.4% and 2.1% previously.
- Mexico is projected to contract by 1.3% in 2025 and 0.6% in 2026.
- Canada’s growth slows to 0.7% for both years.
-
Europe and China more resilient:
- Euro area forecast to grow 1.0% in 2025 and 1.2% in 2026.
- China’s growth raised to 4.8% in 2025, slowing to 4.4% in 2026.
-
It estimated an increase in bilateral tariffs permanently by 10 percentage points would shave around
- 0.3 percentage points off global growth by the second and third years of the shock
- Global inflation would be on average 0.4 percentage points higher over the first three years.
- U.S. economy with growth 0.7 percentage points lower than what it otherwise would have been by the third year.
Trump trade war to sap Canadian, Mexican and US growth, OECD says | Reuters.
https://www.oecd.org/en/about/news/press-releases/2025/03/global-economic-outlook-uncertain-as-growth-slows-inflationary-pressures-persist-and-trade-policies-cloud-outlook.html
IMF April 2025 Update
Growth
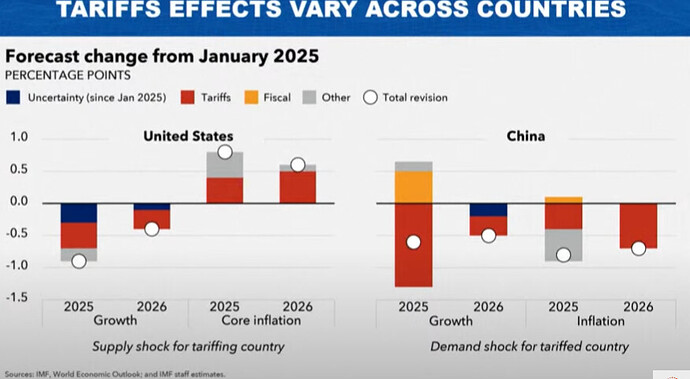
The downgrades are broad-based across countries and reflect in large part the direct effects of the new trade measures and their indirect effects through trade linkage spillovers, heightened uncertainty, and deteriorating sentiment.
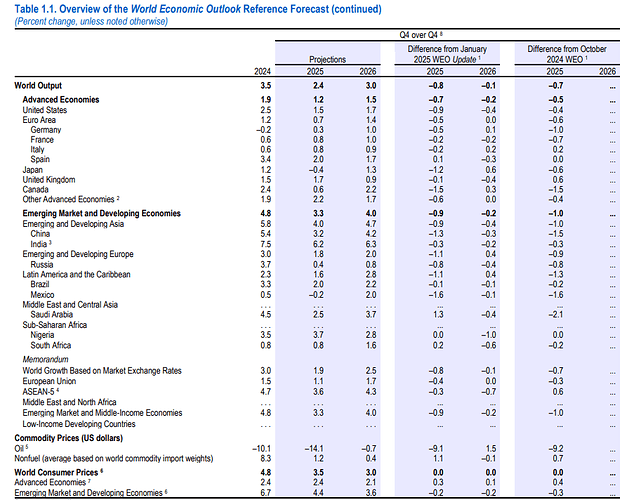
- Global growth is projected to slow from 3.3% in 2024 to 2.8% in 2025, then edge up to 3.0% in 2026. The long-term trend remains subdued at ~3.2% through 2030, below the pre-pandemic average of 3.7%, as aging populations and weak investment constrain momentum.
- US growth is expected to drop to 1.8% in 2025—1 percentage point below 2024 and 0.9 points lower than January’s forecast. While recession isn’t the base case, the risk has risen from 25% to 40%.
- Europe growth is seen dipping to 0.8% in 2025, before a modest recovery to 1.2% in 2026.
- China 2025 GDP growth has been revised down to 4.0% from 4.6% in January.
Inflation
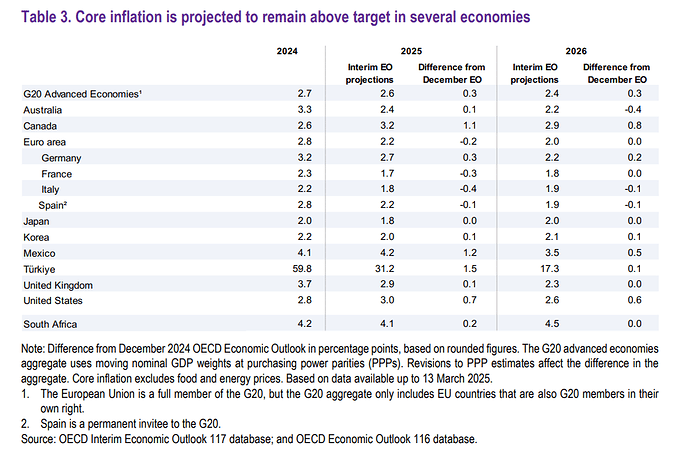
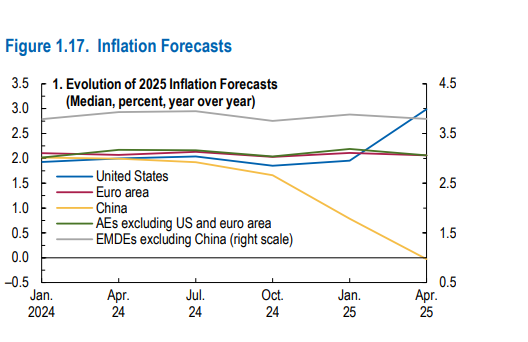
- Global headline inflation expected at 4.3% in 2025.
- US inflation revised up by 1.0 ppt due to tariffs and services price stickiness.
- Inflation pressures in emerging markets are mixed, with China showing deflationary tendencies.
Dollar
- Despite talk of de-dollarization, the dollar remains dominant: In global reserves, cross-border lending, and trade invoicing.
- Rising U.S. term premiums and policy uncertainty do not yet threaten this position.
https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/Issues/2025/04/22/world-economic-outlook-april-2025
OECD lowered its growth forecast for US to 1.6% in 2025 and 1.5% in 2026 from 2.2% and 1.6% respectively
- OECD lowered its growth forecast for US to 1.6% in 2025 and 1.5% in 2026 from 2.2% and 1.6% respectively.
- It lowered its growth forecast for the global economy to 2.9% in 2025 and 2026 from 3.1% and 3.0% respectively due to tariff and policy uncertainty.
- OECD reiterated its growth forecast for the euro area at 1.0% in 2025 and 1.2% in 2026.