Trump has created the Department of Government Efficiency, led by Elon Musk and entrepreneur Vivek Ramaswamy
This is not an official department but more of an advisory role. Trump is seeking an entrepreneurial approach to Government with this.
Musk has set a goal of $2 trillion in spending cuts.
Government spending cuts are likely to exert deflationary and recessionary pressure in the short term , primarily because government expenditures and payrolls play a significant role in supporting current economic activity.
- 2 trillion would be ~20% reduction to government spending, and represent about ~7% of GDP.
In the long term, however, these cuts would offer substantial benefits by addressing the U.S.'s challenging fiscal situation. That said, I’m skeptical about the likelihood of achieving any impactful cuts that could meaningfully alter the fiscal outlook. Here are my reasons:
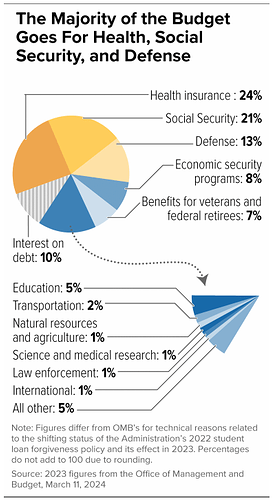
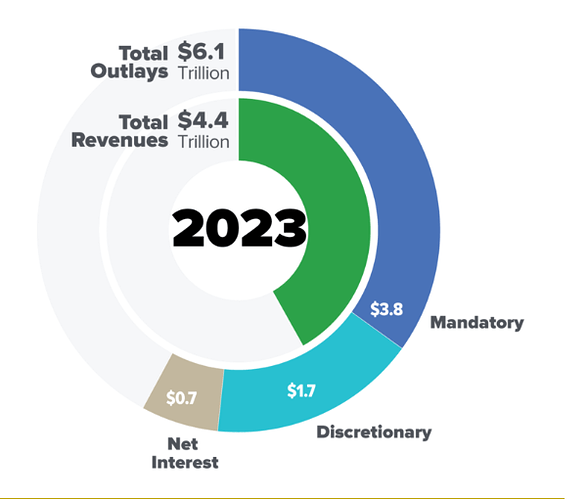
- Approximately $3.8 trillion, or about 62% of the U.S. government’s $6.1 trillion budget, is classified as mandatory spending, with the majority directed to social security programs. Reducing these would require Congressional approval, and despite the Republican majority, significant cuts to these programs are unlikely imo due to their unpopularity and the short-term negative economic impacts that would have.
- Interest payments account for roughly $700 billion (around 11.5%) of the budget in 2023 and will likely continue to rise as existing debt is refinanced at higher interest rates. It increased to $882 billion to FY2024.
- Of the remaining $1.7 trillion discretionary, about $800 billion is allocated to defense spending, which is an area former President Trump and others are looking to increase rather than cut.
- This leaves around $900 billion in discretionary spending that could theoretically be reduced. However, even a 25% reduction (a high assumption since there are some important departments there) would only be $225 billion in annual savings, amounting to just 3.5% of the total budget.
- If we see it from the employee’s side, there are about 3 million federal employees and an additional 4 million contractors. Even if 2 million jobs were cut, a drastic move that would most likely increase unemployment considerably (current unemployed count is only ~6 million), the savings would total around $400 billion per year (assuming an average cost of $200k per position), which is about 6.5% of the budget. This still falls significantly short of a $2 trillion reduction target.
In conclusion, I think potential cuts could be in the range of $100-400 billion per year, with a higher probability to be around the lower range, which would be far from improving significantly the debt situation, in FY2024 the fiscal deficit was $1.8 Trillion.
Ultimately, I believe that greater austerity is always beneficial, and we can hope that efforts to boost productivity and reduce inefficiencies in government spending will have at least some positive results. However, I doubt these measures will be sufficient to meaningfully improve the long-term U.S. debt outlook. Especially as other proposed policies, particularly the proposed tax cuts will likely offset some, all, or even exceed fiscal gains from these spending reductions.