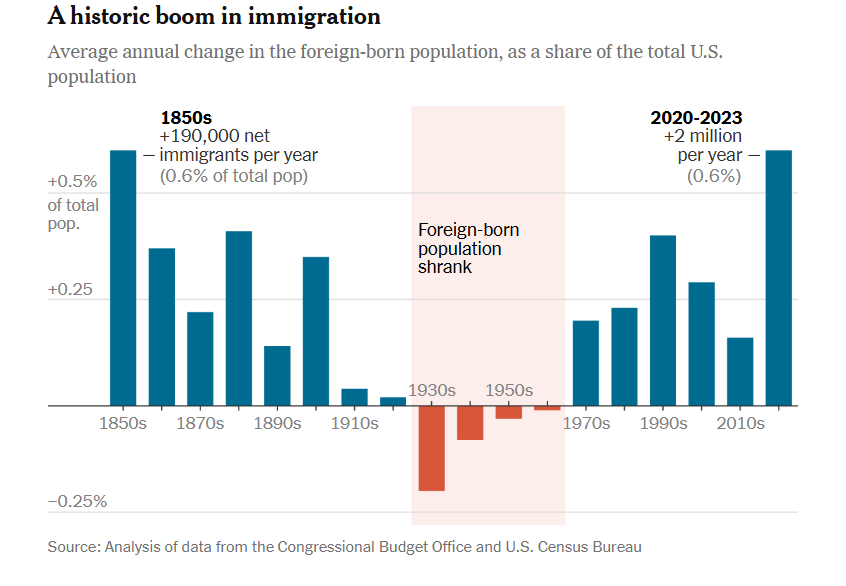
The immigration surge since 2021 has been one of the largest in U.S. history
Immigration has been recognized as a significant driver of growth and productivity in recent years. It has also contributed positively to easing inflationary pressures by addressing challenges associated with labor shortages.
However, Trump has proposed measures aimed at curbing immigration into the United States. These policies, if implemented, could have both inflationary and recessionary effects, making it essential to closely monitor developments and policy changes in this area.
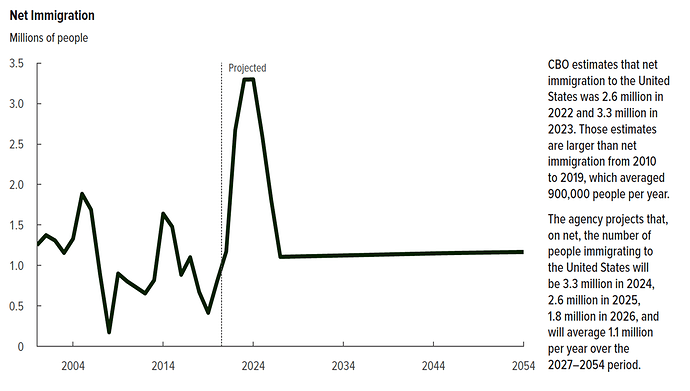
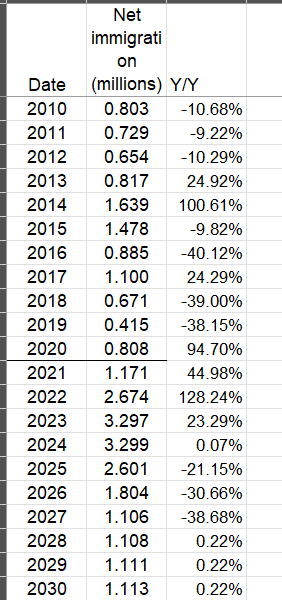
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) has already incorporated reduced immigration into its forecasts for the coming years. However, stricter immigration policies could exacerbate this trend, potentially having economic impacts. However, further research is necessary to better understand the potential consequences of such policies on growth, inflation, and labor market dynamics.
Even after adjusting for today’s larger population, the surge is slightly larger than that during the peak years of Ellis Island traffic
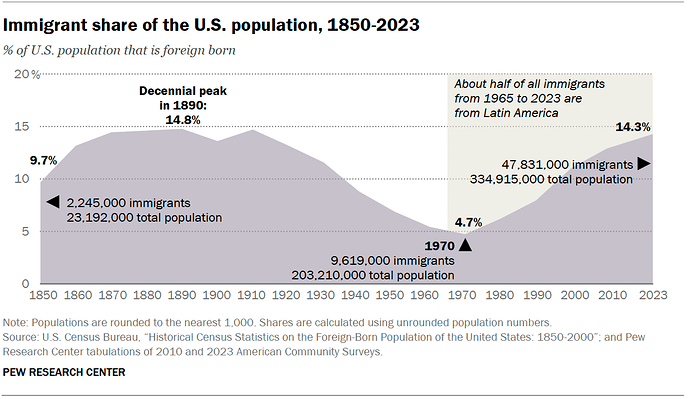
Overall, a record 47.8 million immigrants lived in the U.S. in 2023, up from 46.2 million in 2022.
- Immigrants accounted for 14.3% of the total U.S. population in 2023 – up roughly threefold from 4.7% in 1970, but still below the record high of 14.8% in 1890.